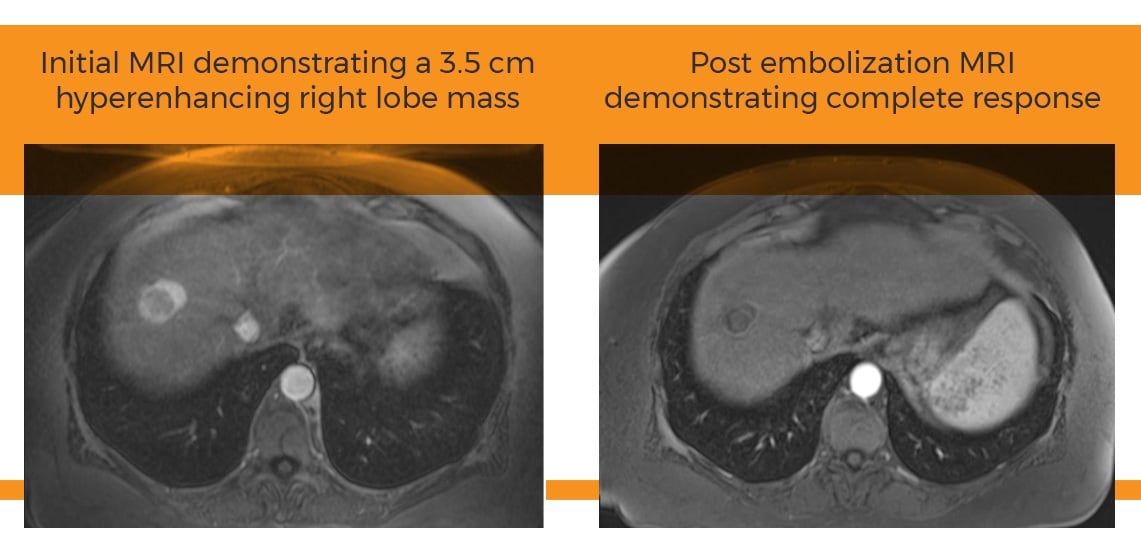
A single-center retrospective evaluation of 22 patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who underwent drug-eluting bead trans-arterial chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) procedures delivered with the Surefire® Infusion System (SIS) demonstrated a complete response in 32% of patients and an overall response rate of 91% after a single treatment session. In comparison, current literature demonstrates an overall response rate of 50-70% in HCC patients treated with multiple sessions of TACE, <10% complete response after one treatment.1,2,3
Why does this matter for physicians?
Response after TACE in HCC has been shown to be correlated with patient survival.4 In the past, efforts to improve TACE response in HCC have been focused on bead types and administered chemotherapy. Recently, there has been growing interest in investigating the impact of the delivery system on TACE response. A few studies from Japan have reported the use of occlusive balloon catheters to improve lipiodol deposition in tumors during conventional TACE.5 This is the first published study that demonstrates how using the SIS to deliver DEB-TACE in HCC patients resulted in a higher initial response rate after just one treatment, compared to multiple treatments in published literature. Even more impressive, 11 out of 12 (92%) study participants who initially had tumor burden outside of UNOS transplant criteria were successfully downstaged after one treatment.
How does the Surefire Infusion System enable this result?
Due to the aberrant nature of tumor vasculature, the current standard endpoint for TACE (stasis or sub-stasis) may occur before the tumor bed is completely saturated with the therapeutic agent, resulting in suboptimal tumor response rates. The SIS enables physicians to safely administer therapy using temporary increases in pressure during infusion to ensure the optimal endpoint is reached during TACE. As a result, the SIS enables improved tumor uptake with deeper particle penetration than a standard micro-catheter. The study authors share best practices to achieve an optimal embolization endpoint with the SIS.
What does this mean for patients?
While most response rates are taken after multiple treatments and follow-ups, this study describes response rates after one single DEB-TACE treatment using the SIS. These preliminary findings suggest that DEB-TACE with the SIS may improve response rates after TACE and provide therapeutic benefit for patients with HCC. Additionally, the study showed no increase in drug-induced liver damage compared to current standards, which demonstrates an increase in response rate without compromising patient safety.
For a more in-depth clinical review, view Dr. Alexander Kim’s recorded presentation here.
1 Lammer J, Malagari K, Vogl T, Pilleul F, Denys A, Watkinson A, et al. Prospective randomized study of doxorubicin-eluting-bead embolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: results of the PRE- CISION V study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33: 41–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009- 9711-7 PMID: 19908093
2 Reyes DK, Vossen JA, Kamel IR, Azad NS, Wahlin TA, Torbenson MS, et al. Single-center phase II trial of transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: initial experience in the United States. Cancer J Sudbury Mass. 2009; 15: 526–532. https:// doi.org/10.1097/PPO.0b013e3181c5214b PMID: 20010173
3 Lewandowski RJ, Mulcahy MF, Kulik LM, Riaz A, Ryu RK, Baker TB, et al. Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: comprehensive imaging and survival analysis in a 172-patient cohort. Radiol- ogy. 2010; 255: 955–965. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10091473 PMID: 20501733
4 Kim BK, Kim KA, Park JY, Ahn SH, Chon CY, Han K-H, et al. Prospective comparison of prognostic val- ues of modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours with European Association for the Study of the Liver criteria in hepatocellular carcinoma following chemoembolisation. Eur J Cancer Oxf Engl 1990. 2013; 49: 826–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2012.08.022
5 Irie T, Kuramochi M, Takahashi N. Dense accumulation of lipiodol emulsion in hepatocellular carcinoma nodule during selective balloon-occluded transarterial chemoembolization: measurement of balloon- occluded arterial stump pressure. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013; 36: 706–713. https://doi.org/10. 1007/s00270-012-0476-z PMID: 22996589